Unveiling The Cone: A Deep Dive Into Conical Map Projections
Unveiling the Cone: A Deep Dive into Conical Map Projections
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Cone: A Deep Dive into Conical Map Projections
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Unveiling the Cone: A Deep Dive into Conical Map Projections. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Cone: A Deep Dive into Conical Map Projections
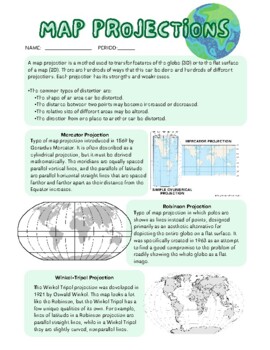
Map projections are the basic instruments that translate the three-dimensional floor of the Earth onto a two-dimensional aircraft. This inherently entails distortion, because it’s inconceivable to completely symbolize a sphere on a flat floor with out compromising space, form, distance, or route. Among the many varied projection varieties, conical projections supply a compelling steadiness of those distortions, making them appropriate for a spread of cartographic functions. This text delves into the intricacies of conical map projections, exploring their geometry, properties, varieties, benefits, limitations, and functions.
The Geometry of Conical Projections:
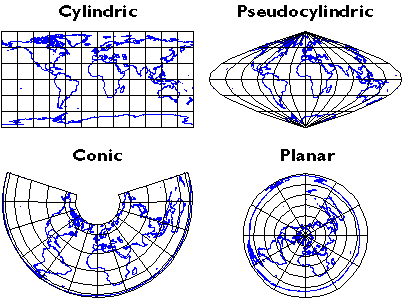
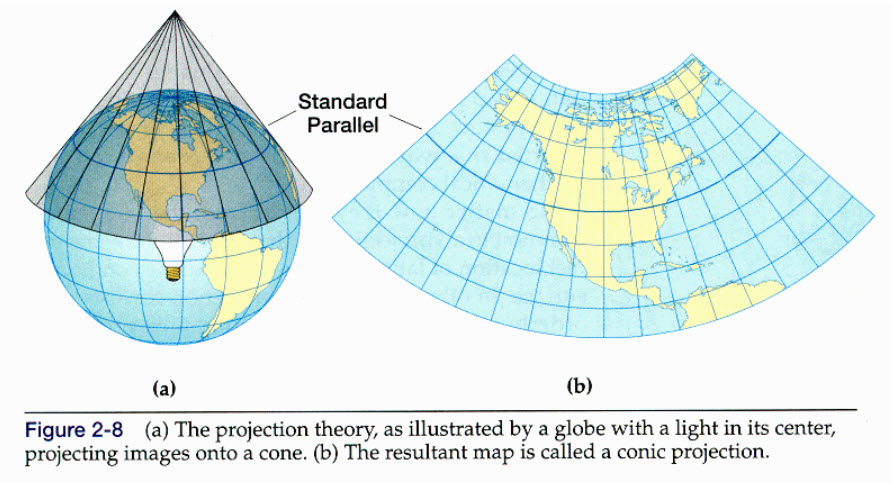
Conical projections, because the title suggests, make use of a cone because the middleman floor onto which the Earth’s floor is projected. Think about a cone positioned over the globe, tangential to or secant to (intersecting) a selected parallel of latitude. The meridians are projected onto straight traces radiating from the apex of the cone, whereas the parallels of latitude are projected onto concentric circles across the apex. The projection’s accuracy is basically decided by the connection between the cone and the globe.
-
Tangential Cones: These cones contact the globe at a single customary parallel. Distortion is minimal alongside this parallel, but it surely will increase progressively as you progress away from it.
-
Secant Cones: These cones intersect the globe at two customary parallels. This introduces distortion at each parallels, but it surely reduces the distortion within the space between them. The area between the usual parallels usually displays much less distortion than a tangential cone projection.
The selection between a tangential and a secant cone considerably impacts the projection’s accuracy and the extent of its distortion. Secant cones usually supply a greater compromise for bigger areas, minimizing general distortion in comparison with tangential cones.
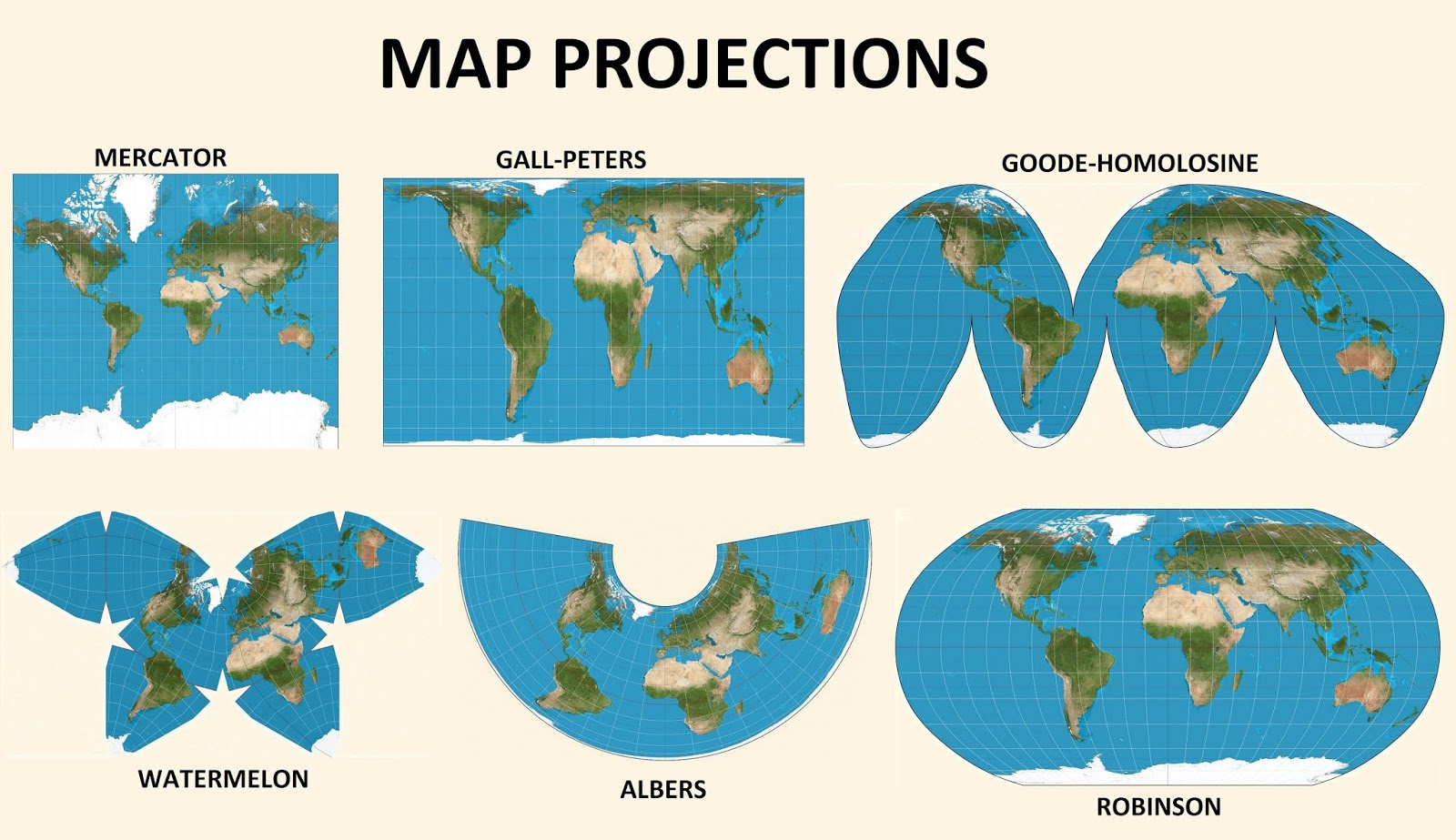
Sorts of Conical Projections:
A number of variations of conical projections exist, every with distinctive traits and functions:
-
Easy Conical Projection: That is essentially the most fundamental type, projecting meridians onto straight traces converging on the apex and parallels onto concentric circles. It is a tangential projection, which means it is solely correct alongside the usual parallel. Distortion will increase considerably as you progress away from this parallel.
-
Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection maintains the form of small areas, making it conformal. It is broadly used for mapping mid-latitude areas as a result of it minimizes angular distortion. Each tangential and secant variations exist, with secant variations providing higher general accuracy for bigger areas. The Lambert Conformal Conic projection is continuously used for aeronautical charts and topographic maps.
-
Albers Equal-Space Conic Projection: This projection preserves space, making certain that the relative sizes of areas are precisely represented. It is generally used for thematic maps the place the world of options is essential, similar to inhabitants density maps or useful resource distribution maps. Just like the Lambert projection, it may be tangential or secant.
-
Polyconic Projection: This projection makes use of a collection of cones, every tangent to a single parallel of latitude. This leads to a projection the place the meridians are curved, and the parallels of latitude are concentric circles solely across the central meridian. It is helpful for mapping areas with vital east-west extent, though distortion might be vital at increased latitudes. It is much less generally used now because of the availability of extra correct projections.
-
Modified Conical Projections: Many variations and modifications of those fundamental conical projections exist. These modifications typically contain adjusting parameters to optimize the projection for particular areas or functions. For instance, some modifications may incorporate particular formulation to attenuate distortion particularly areas of curiosity.
Benefits of Conical Projections:
Conical projections supply a number of benefits over different projection varieties:
-
Good illustration of mid-latitude areas: They excel at mapping areas that span a big vary of longitude however a comparatively smaller vary of latitude, significantly mid-latitude areas.
-
Stability of distortions: Whereas no projection can eradicate all distortion, conical projections supply a comparatively good steadiness between space, form, distance, and route distortion. Secant cones, particularly, present a greater steadiness than tangential cones.
-
Simplicity of development: The underlying geometry is comparatively easy, making them simpler to assemble and perceive in comparison with another extra complicated projections.
-
Appropriate for varied functions: Their properties make them appropriate for a variety of functions, from topographic mapping to thematic mapping and aeronautical charting.
Limitations of Conical Projections:
Regardless of their benefits, conical projections have limitations:
-
Elevated distortion at increased latitudes: Distortion will increase considerably as you progress away from the usual parallel(s), significantly at increased latitudes. This makes them much less appropriate for mapping polar areas or areas extending far north or south.
-
Not best for world maps: Their inherent geometry makes them unsuitable for representing all the globe precisely. The distortion turns into extreme on the edges of the projection.
-
Meridian convergence: The convergence of meridians on the apex can result in distortions in form and space, significantly close to the apex.
Purposes of Conical Projections:
Conical projections discover software in numerous fields:
-
Topographic Mapping: The Lambert Conformal Conic projection is broadly used for topographic maps, significantly at mid-latitudes, resulting from its preservation of form.
-
Aeronautical Charts: The Lambert Conformal Conic projection can also be extensively utilized in aeronautical charts due to its correct illustration of route.
-
Thematic Mapping: The Albers Equal-Space Conic projection is most well-liked for thematic maps the place space preservation is essential, similar to maps displaying inhabitants density or useful resource distribution.
-
Atlases: Conical projections continuously seem in atlases, significantly for regional maps of mid-latitude areas.
-
Navigation: Sure conical projections, resulting from their relative accuracy in distance and route, have been used for navigational functions, although extra subtle techniques are actually predominantly used.
Selecting the Proper Conical Projection:
The collection of an acceptable conical projection relies upon closely on the particular software and the area being mapped. Think about the next elements:
-
Space of curiosity: The extent and latitude of the area will considerably affect the selection of projection. Secant cones are usually most well-liked for bigger areas.
-
Kind of map: Thematic maps typically require equal-area projections (like Albers), whereas topographic maps profit from conformal projections (like Lambert).
-
Emphasis on particular properties: If correct illustration of form is paramount, a conformal projection is critical. If space preservation is vital, an equal-area projection is required.
Conclusion:
Conical map projections symbolize a precious software within the cartographer’s arsenal. Their potential to steadiness varied distortions, coupled with their relative simplicity, makes them appropriate for a variety of functions. Understanding the geometry, properties, and limitations of various conical projections is important for choosing essentially the most acceptable projection for a given activity, making certain correct and efficient communication of spatial data. The continuing improvement and refinement of conical projections, alongside developments in GIS and mapping applied sciences, proceed to increase their utility and applicability in varied fields. As expertise advances, we are able to count on additional refinements and doubtlessly new variations of conical projections to emerge, additional enhancing their capabilities and addressing particular cartographic wants.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Unveiling the Cone: A Deep Dive into Conical Map Projections. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!