The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout A Continent
The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout a Continent
Associated Articles: The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout a Continent
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout a Continent. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout a Continent

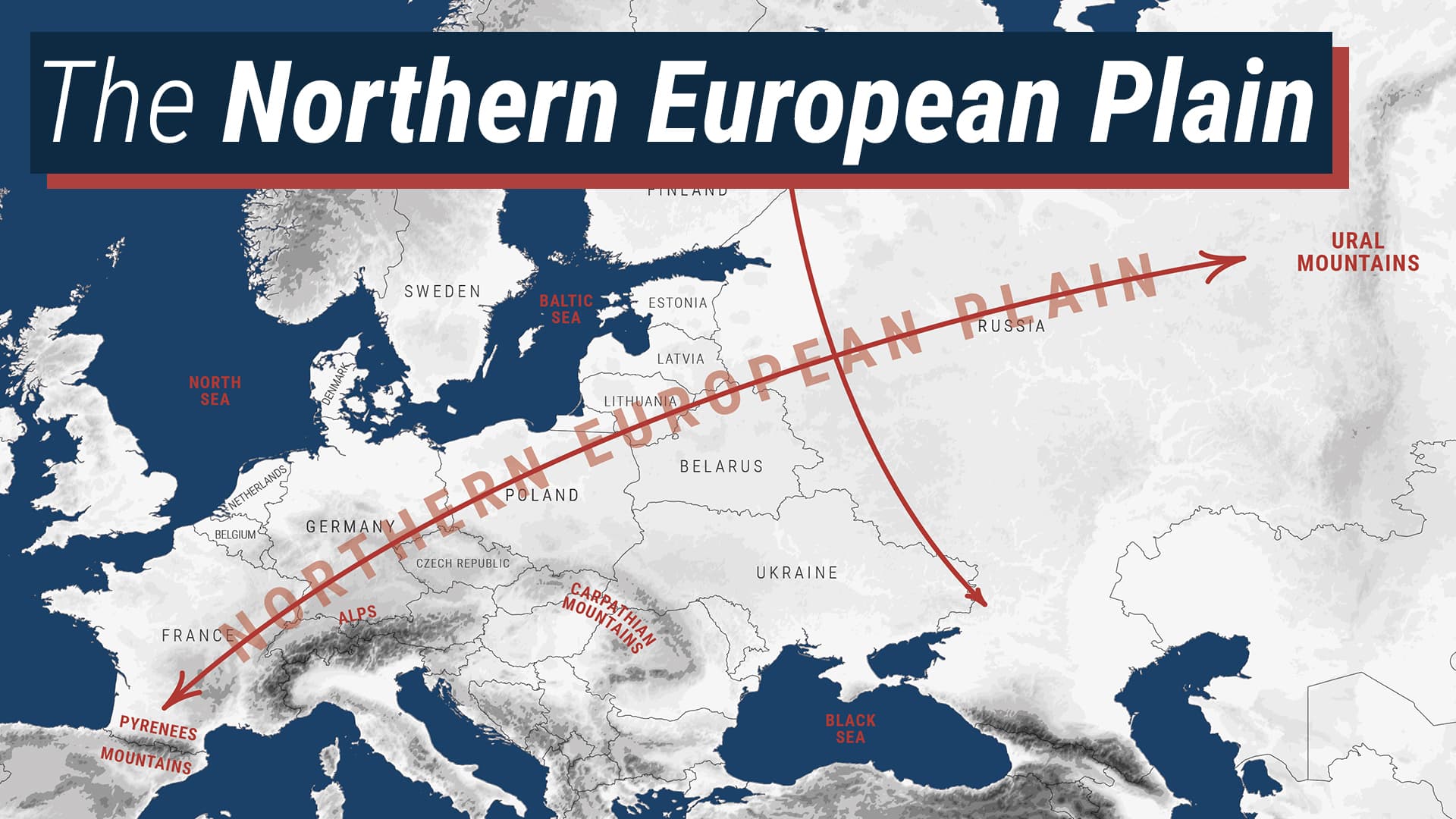
The Northern European Plain, an enormous expanse of comparatively flat land stretching throughout northern Europe, is a area of immense geographic and historic significance. Its fertile soils, navigable rivers, and comparatively temperate local weather have formed the event of quite a few societies, leaving an indelible mark on the continent’s political, financial, and cultural panorama. Understanding its geographical traits, its influence on human settlement, and the challenges it faces in the present day requires an in depth examination, finest understood together with a map. (Think about a map right here, exhibiting the extent of the Northern European Plain, encompassing components of Poland, Germany, Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, and lengthening into northern Russia and the Baltic states. The map ought to spotlight main rivers just like the Vistula, Oder, Elbe, Rhine, and Volga, in addition to key cities and geographical options).
Geographical Boundaries and Traits:
Defining the exact boundaries of the Northern European Plain is a posh activity, because the transition to surrounding highlands is gradual moderately than abrupt. Typically, it is thought of to increase from the foothills of the Scandinavian Mountains within the north and east, to the Central Uplands of Germany and the Carpathian Mountains within the south and east. Westward, it reaches the North Sea and Atlantic coasts, whereas eastward it stretches into the huge Russian Plain, ultimately merging with the West Siberian Plain.
The plain’s topography is characterised by its low reduction. Elevations hardly ever exceed 300 meters (984 toes) above sea degree, creating a comparatively flat and gently undulating panorama. This low-lying nature has considerably impacted drainage patterns, leading to a dense community of rivers and wetlands. Many of those rivers are navigable, serving as essential transportation arteries all through historical past and persevering with to play a significant position in trendy commerce.
The main river methods that dissect the plain are pivotal to its character. The Vistula, Oder, and Elbe rivers drain the jap and central parts, flowing into the Baltic Sea. The Rhine, a significant European waterway, flows westward via the Netherlands and into the North Sea, whereas the Volga, Europe’s longest river, traverses the easternmost extent of the plain in Russia, ultimately emptying into the Caspian Sea. These rivers, together with their tributaries, have fostered fertile alluvial plains, offering wealthy agricultural land and supporting numerous ecosystems.
The geological historical past of the plain is equally important. Intensive glacial exercise in the course of the Pleistocene epoch formed the panorama, forsaking deposits of fertile glacial until, sand, and gravel. These deposits created fertile soils, superb for agriculture, notably within the areas coated by loess, a fine-grained windblown sediment. The presence of peat bogs and wetlands, remnants of glacial exercise and riverine processes, provides to the range of the panorama.
Human Influence and Settlement:
The Northern European Plain’s fertile soils and considerable sources have attracted human settlement for millennia. Its flat terrain facilitated agricultural practices, permitting for large-scale cultivation and the event of intensive farming methods. The navigable rivers supplied environment friendly transportation routes, fostering commerce and communication between completely different settlements. These elements mixed to create favorable situations for the expansion of enormous, interconnected populations and the rise of highly effective states.
The area has witnessed the rise and fall of quite a few empires and civilizations. From the early Slavic settlements to the Hanseatic League, the Roman Empire’s affect in its western reaches, and the growth of varied Germanic kingdoms, the plain has been a stage for important historic occasions. Main cities, corresponding to Berlin, Warsaw, Amsterdam, Hamburg, and lots of others, have emerged as facilities of commerce, tradition, and political energy, their development inextricably linked to the plain’s sources and strategic location.
The Industrial Revolution additional remodeled the Northern European Plain. Its wealthy coal deposits, notably in areas just like the Ruhr in Germany, fueled industrial development, resulting in the institution of main industrial facilities and the event of a posh community of transportation infrastructure. This era noticed fast urbanization and inhabitants development, reworking the panorama with factories, mines, and increasing cities.
Fashionable Challenges and Conservation:
Regardless of its historic significance and financial significance, the Northern European Plain faces quite a few challenges within the twenty first century. Intensive agriculture, whereas contributing to meals manufacturing, has resulted in soil degradation, water air pollution from fertilizers and pesticides, and biodiversity loss. City sprawl continues to devour useful agricultural land and fragment pure habitats.
Local weather change poses a big menace, with rising sea ranges threatening coastal areas and altered precipitation patterns impacting agricultural yields. Elevated frequency and depth of maximum climate occasions, corresponding to floods and droughts, additional exacerbate these challenges. Conservation efforts are essential to preserving the plain’s biodiversity, defending its water sources, and mitigating the impacts of local weather change. Sustainable agricultural practices, improved water administration, and the creation of protected areas are important steps in the direction of guaranteeing the long-term sustainability of this very important area.
Conclusion:
The Northern European Plain is a area of immense geographic and historic significance. Its fertile soils, navigable rivers, and comparatively flat terrain have formed the event of quite a few societies, contributing considerably to Europe’s financial and cultural panorama. Nevertheless, the plain faces important challenges within the twenty first century, requiring cautious administration and conservation efforts to make sure its continued prosperity and the preservation of its wealthy pure heritage. Understanding its geographical traits, historic evolution, and up to date challenges is essential for growing efficient methods to handle this very important area and guarantee its sustainability for future generations. A radical examination, all the time supported by an in depth map illustrating its geographical options and the distribution of human settlements, gives the required context for appreciating the complexities and significance of this significant European plain.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into The Northern European Plain: A Geographic Tapestry Woven Throughout a Continent. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!