The North Pole: A Geographic And Geopolitical Iceberg
The North Pole: A Geographic and Geopolitical Iceberg
Associated Articles: The North Pole: A Geographic and Geopolitical Iceberg
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The North Pole: A Geographic and Geopolitical Iceberg. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The North Pole: A Geographic and Geopolitical Iceberg
The North Pole, the northernmost level on Earth, holds a singular and fascinating place in our world. Greater than only a geographical marker, it is a focus for scientific analysis, geopolitical maneuvering, and environmental considerations. This text will delve into the multifaceted nature of the North Pole, exploring its geography, local weather, historical past, and the escalating significance it holds within the twenty first century.
Geographical Location and Defining the Pole:
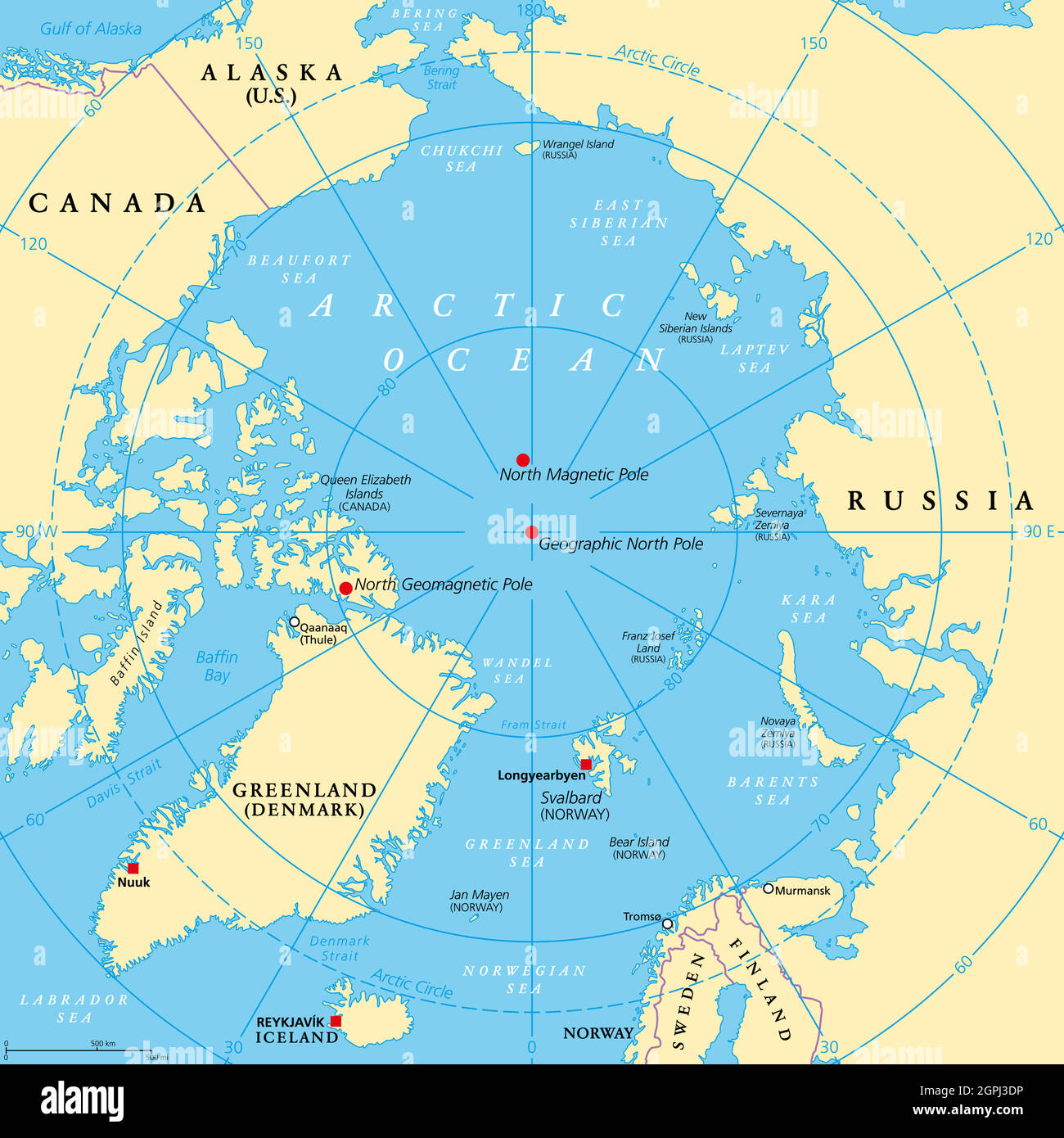
Not like the South Pole, which resides on a landmass (Antarctica), the North Pole is situated in the midst of the Arctic Ocean. This floating sea ice, continually shifting and reforming, makes the exact location of the North Pole a dynamic entity. There isn’t any mounted landmass to mark it; as an alternative, the pole is outlined by the convergence of Earth’s strains of longitude. Because of this the exact coordinates are continually altering, albeit inside a comparatively small radius, influenced by the motion of the ice pack. This fluidity necessitates using GPS expertise and steady monitoring to pinpoint the precise location at any given time.
The encircling Arctic Ocean is a comparatively shallow sea, averaging round 1,000 meters (3,300 toes) in depth, considerably shallower than the deep ocean basins discovered elsewhere. Beneath the ice and water lies the Arctic seabed, a area of appreciable geological curiosity, containing huge reserves of pure sources, as we’ll focus on later.
Local weather and Environmental Situations:
The North Pole’s local weather is characterised by excessive chilly, darkness for half the 12 months (polar night time), and daylight for the opposite half (polar day). Temperatures usually hover round -40°C (-40°F) and even decrease, although variations exist relying on the time of 12 months and the presence of open water. The ocean ice performs an important function in regulating the Arctic’s local weather, reflecting daylight again into house and influencing world climate patterns. Nonetheless, the speedy decline in sea ice extent and thickness resulting from local weather change is a significant concern, with important repercussions for the worldwide local weather system.
The melting sea ice results in a constructive suggestions loop: because the ice melts, darker ocean water absorbs extra photo voltaic radiation, accelerating additional ice soften. This contributes to rising sea ranges globally and alters ocean currents, impacting climate patterns worldwide. The shrinking ice additionally impacts Arctic wildlife, comparable to polar bears, seals, and walruses, whose survival is determined by the ocean ice for searching and breeding.
Historical past and Exploration:
The search to achieve the North Pole has captivated explorers for hundreds of years. Early expeditions, typically fraught with hardship and lack of life, tried to achieve the pole utilizing dogsleds, ships, and even submarines. Whereas claims of reaching the North Pole within the late nineteenth and early Twentieth centuries are sometimes debated as a result of difficulties of correct navigation on the time, Robert Peary’s 1909 expedition is mostly accepted as the primary profitable attainment of the North Pole, although controversies persist relating to the accuracy of his claims.
The arrival of air journey considerably altered the exploration of the Arctic. Flights over the North Pole grew to become commonplace within the mid-Twentieth century, facilitating scientific analysis and establishing the pole’s strategic significance. The institution of ice-breaking ships and superior navigational expertise additional enhanced entry to the area, although navigating the treacherous ice circumstances stays a major problem.
Geopolitical Significance:
The North Pole’s strategic significance has grown exponentially in current a long time. The melting Arctic ice has opened up new transport routes, considerably decreasing journey instances between Asia and Europe. This "Northern Sea Route" provides substantial financial advantages, doubtlessly revolutionizing world commerce. Nonetheless, this additionally raises geopolitical tensions, as international locations vie for management of those important waterways and the sources they unlock.
Moreover, the Arctic seabed is believed to carry huge reserves of oil, pure fuel, and different beneficial minerals. The United Nations Conference on the Regulation of the Sea (UNCLOS) permits coastal states to say prolonged continental cabinets, doubtlessly granting them rights to take advantage of sources past their conventional territorial waters. A number of Arctic nations, together with Russia, Canada, Denmark (through Greenland), Norway, and the US (through Alaska), are actively pursuing claims based mostly on UNCLOS, resulting in overlapping claims and potential conflicts.
The army implications are additionally important. The diminished ice cowl permits for elevated army exercise within the Arctic, together with the deployment of naval vessels and the institution of army bases. This elevated army presence underscores the rising geopolitical competitors for management of the Arctic area.
Scientific Analysis on the North Pole:
The North Pole serves as an important web site for scientific analysis, notably within the fields of local weather change, oceanography, and atmospheric science. Researchers monitor sea ice extent and thickness, examine ocean currents, and analyze atmospheric composition to grasp the impacts of local weather change and its world penalties. The distinctive atmosphere of the Arctic supplies beneficial insights into the Earth’s local weather system and its response to human actions.
Analysis stations and icebreakers conduct numerous scientific experiments, gathering knowledge on sea ice dynamics, ocean currents, atmospheric circumstances, and the consequences of local weather change on the Arctic ecosystem. This knowledge is essential for growing local weather fashions, predicting future local weather eventualities, and informing coverage choices associated to local weather change mitigation and adaptation. Worldwide collaborations are important in coordinating analysis efforts and sharing knowledge to realize a complete understanding of the Arctic’s complicated atmosphere.
Environmental Considerations and Conservation Efforts:
The Arctic is among the many areas most weak to local weather change. The speedy melting of sea ice poses a major menace to the Arctic ecosystem and has far-reaching world penalties. The lack of sea ice impacts wildlife, alters ocean currents, and contributes to rising sea ranges. Moreover, air pollution from industrial actions and transport poses a critical menace to the Arctic atmosphere.
Worldwide cooperation is important to deal with the environmental challenges going through the Arctic. Efforts are underway to cut back greenhouse fuel emissions, defend Arctic wildlife, and mitigate the impacts of air pollution. The Arctic Council, an intergovernmental discussion board, performs an important function in coordinating worldwide efforts to guard the Arctic atmosphere and promote sustainable improvement.
The Way forward for the North Pole:
The North Pole’s future is inextricably linked to the worldwide response to local weather change. The speed of sea ice soften will considerably affect the area’s accessibility, financial potential, and geopolitical dynamics. The continued competitors for sources and strategic benefit would require cautious diplomacy and worldwide cooperation to keep away from battle and make sure the sustainable administration of the Arctic’s sources.
Addressing the environmental challenges going through the Arctic is paramount. Worldwide collaboration is essential to mitigate the impacts of local weather change, defend the distinctive Arctic ecosystem, and make sure the long-term sustainability of the area. The North Pole’s future will depend upon our capability to steadiness the financial alternatives offered by the melting ice with the pressing want to guard this fragile and important atmosphere. The fragile steadiness between exploitation and conservation will outline the character of this pivotal area for generations to return.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into The North Pole: A Geographic and Geopolitical Iceberg. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!