Navigating The Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information To Iteration Methods
Navigating the Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information to Iteration Methods
Associated Articles: Navigating the Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information to Iteration Methods
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information to Iteration Methods. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information to Iteration Methods
Java’s Map interface, a cornerstone of information construction design, offers a strong approach to retailer key-value pairs. Understanding how one can effectively iterate over these maps is essential for any Java developer. This text delves deep into the varied strategies for iterating by Java Maps, evaluating their efficiency traits, and providing sensible examples to information you in selecting the optimum method on your particular wants. We’ll discover the nuances of every strategy, highlighting greatest practices and addressing potential pitfalls.
Understanding the Java Map Interface
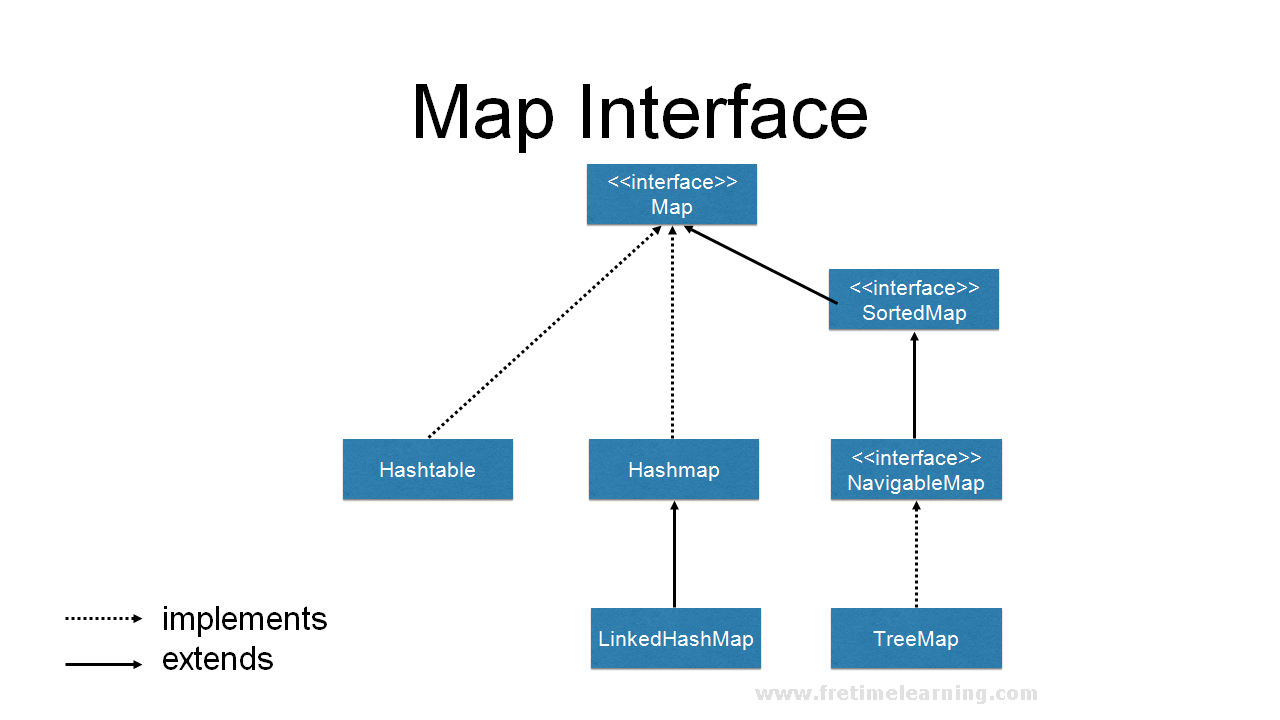
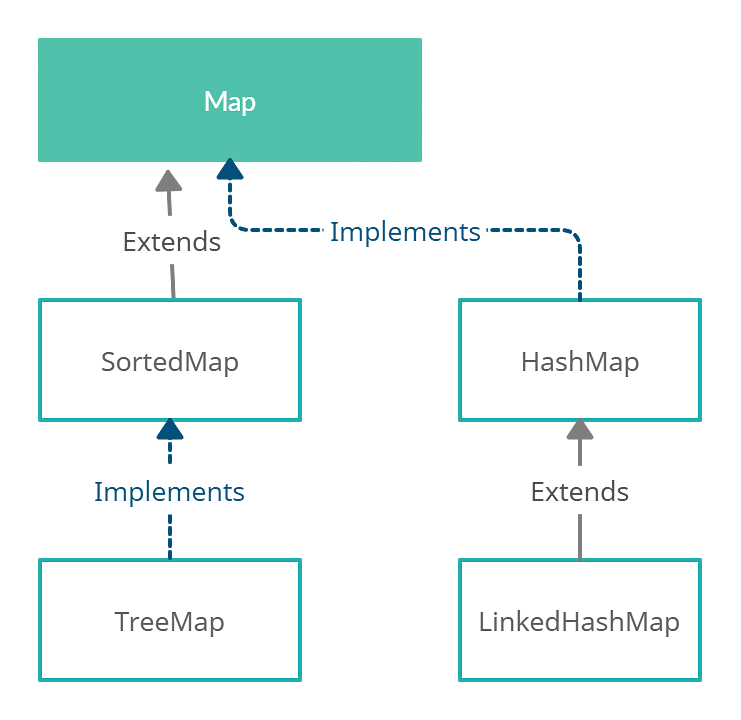
Earlier than diving into iteration methods, let’s briefly overview the Map interface. A Map shops information in key-value pairs, the place every key’s distinctive and maps to a single worth. The Map interface itself would not dictate the underlying implementation; a number of concrete implementations exist, every with its personal strengths and weaknesses relating to iteration efficiency. Frequent implementations embrace:
-
HashMap: Makes use of a hash desk for quick key-value lookups, insertions, and deletions. Iteration order shouldn’t be assured and may change over time. -
TreeMap: Implements a Purple-Black tree, offering sorted key-value pairs primarily based on the pure ordering of the keys or a offeredComparator. Iteration is ordered. -
LinkedHashMap: Maintains insertion order, offering predictable iteration sequences. Efficiency is usually corresponding toHashMap. -
Hashtable: A legacy class much likeHashMap, however synchronized (thread-safe). Iteration is much less environment friendly as a consequence of synchronization overhead.
The selection of map implementation considerably impacts the effectivity of iteration. Understanding these variations is paramount to optimizing your code.
Iteration Methods: A Detailed Exploration
A number of strategies enable iterating over a Java Map. Let’s look at every one intimately, contemplating their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for various situations.
1. Utilizing keySet() and an Enhanced for Loop:
That is arguably the most typical and simple strategy. The keySet() methodology returns a Set containing all of the keys within the map. The improved for loop then iterates over this set, permitting entry to every key, from which you’ll retrieve the corresponding worth utilizing the get() methodology.
Map<String, Integer> myMap = new HashMap<>();
// ... populate myMap ...
for (String key : myMap.keySet())
Integer worth = myMap.get(key);
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Worth: " + worth);
This methodology is straightforward and readable. Nevertheless, it entails a get() name for every key, which might affect efficiency, particularly for big maps. The efficiency overhead stems from the repeated hash desk lookups throughout the get() methodology.
2. Utilizing entrySet() and an Enhanced for Loop:
This strategy presents higher efficiency than utilizing keySet(). The entrySet() methodology returns a Set of Map.Entry objects, every representing a key-value pair. This eliminates the necessity for particular person get() calls, as each the important thing and worth are immediately accessible throughout the loop.
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : myMap.entrySet())
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer worth = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Worth: " + worth);
That is usually the popular methodology for its effectivity and readability. It avoids redundant hash desk lookups and immediately accesses each key and worth.
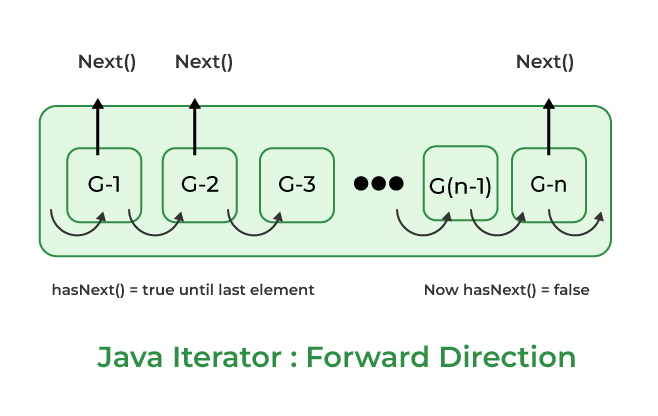
3. Utilizing keySet() and an Iterator:
Whereas much less concise than the improved for loop, utilizing an express Iterator offers extra management over the iteration course of. That is significantly helpful when it’s good to take away parts throughout iteration or deal with exceptions gracefully.
Iterator<String> keyIterator = myMap.keySet().iterator();
whereas (keyIterator.hasNext())
String key = keyIterator.subsequent();
Integer worth = myMap.get(key);
// ... course of key and worth ...
if (/* some situation */)
keyIterator.take away(); // Take away the entry
The flexibility to take away parts throughout iteration is a major benefit. Nevertheless, do not forget that eradicating parts utilizing the iterator is the one secure method to take action throughout iteration; modifying the map immediately can result in unpredictable conduct.
4. Utilizing entrySet() and an Iterator:
Just like utilizing keySet() with an iterator, this strategy offers extra management when iterating over Map.Entry objects.
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entryIterator = myMap.entrySet().iterator();
whereas (entryIterator.hasNext())
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = entryIterator.subsequent();
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer worth = entry.getValue();
// ... course of key and worth ...
if (/* some situation */)
entryIterator.take away(); // Take away the entry
This methodology presents the identical efficiency advantages as utilizing entrySet() with an enhanced for loop, whereas offering the added flexibility of the Iterator interface.
5. Utilizing Streams (Java 8 and above):
Java 8 launched streams, offering a purposeful strategy to information processing. Streams provide a concise and expressive approach to iterate over maps and carry out varied operations.
myMap.entrySet().stream().forEach(entry ->
System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Worth: " + entry.getValue());
);This strategy leverages the facility of parallel processing for probably sooner execution on giant datasets. Nevertheless, the overhead of stream creation may outweigh the advantages for smaller maps. Parallel streams must be used cautiously, contemplating the potential for elevated complexity and overhead.
Efficiency Concerns and Greatest Practices
The selection of iteration methodology considerably impacts efficiency, particularly for big maps. The entrySet() strategy, whether or not utilizing an enhanced for loop or an iterator, usually offers the most effective efficiency as a result of it avoids redundant get() calls. Utilizing streams may also be environment friendly, significantly with parallel processing, however the overhead must be thought-about.
Keep away from modifying the map throughout iteration until you employ an iterator’s take away() methodology. Immediately modifying the map whereas iterating can result in ConcurrentModificationException or unpredictable conduct.
For very giant maps, contemplate optimizing your information constructions and algorithms earlier than focusing solely on iteration methods. Profiling your code can assist establish efficiency bottlenecks and information optimization efforts.
Conclusion
Iterating over Java Maps is a basic activity, and selecting the best method is essential for environment friendly and maintainable code. The entrySet() methodology, mixed with both an enhanced for loop or an iterator, usually presents the most effective steadiness of efficiency and readability. Streams present a strong various for bigger datasets, permitting for parallel processing. Nevertheless, all the time contemplate the particular wants of your software and the dimensions of your map when choosing an iteration methodology. By understanding the nuances of every strategy and following greatest practices, you’ll be able to successfully navigate the Java Map panorama and write high-performing, sturdy code. Bear in mind to profile your code to make sure you’re utilizing essentially the most environment friendly methodology on your particular use case. Selecting the optimum iteration technique is a key factor in writing environment friendly and scalable Java functions.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Navigating the Java Map Panorama: A Complete Information to Iteration Methods. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!